Characteristics of Circular Motion
Characteristics of Circular Motion: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Angular Acceleration,Circular Motion with Variable Angular Acceleration,Linear Velocity in Circular Motion etc.
Important Questions on Characteristics of Circular Motion
Two particles of mass M and m are moving in a circle of radii R and r. If their time – periods are same, what will be the ratio of their linear velocities?
What is the linear velocity if the angular velocity vector is and position vector is ?
A body is whirled in a horizontal circle of radius 20 cm. It has an angular velocity of What is its linear velocity at any point on circular path
When a body moves with a constant speed along a circle
A particle of mass M is moving in a horizontal circle of radius R with uniform speed V. When it moves from one point to a diametrically opposite point, its :
A hemispherical bowl of radius is rotating about its own axis (which is vertical), with an angular velocity . A particle of mass on the frictionless inner surface of the bowl is also rotating with the same . The particle is at a height from the bottom of the bowl.
Obtain the relation between and . What is the minimum value of needed, in order to have a non-zero value of ?
An electric line of force in the plane is given by the equation . A particle with unit positive charge, initially at rest at the point in the plane, will move along the circular line of force.
The tangential acceleration of the tip of a blade is and its centripetal acceleration is . Find the value of linear acceleration of the tip of the blade.
Why is centrifugal force considered as an imaginary force?
A body of mass is moving with speed along a circular path of radius . Now, the speed is reduced to and radius is increased to . For this change, initial centripetal force needs to he
A particle is moving in a circle of radius with a constant speed . Its average acceleration over the time when it moves over half the circle is :
The angular acceleration of a body, moving along the circumference of a circle, is:
Two identical particles each of mass go round a circle of radius under the action of their mutual gravitational attraction. The angular speed of each particle will be :
A child of mass is going round a merry-go-round that makes rotation in . The radius of the merry-go-round is . The centrifugal force on the child will be
A particle is moving with constant speed in a circular path. When the particle turns by an angle the ratio of instantaneous velocity to its average velocity is The value of will be
Vikas is driving a car of mass m along a circular path of radius The coefficient of static friction between the path and tyres of the car is .The maximum speed with which he can drive the car without slipping is ( is acceleration due to gravity)
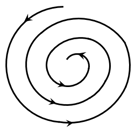
A particle is moving on a spiral path as shown in the figure. The speed of particle remains constant.
In circular motion speed depends on angular position as . The value of as a function of time is
A car is moving with a speed of on a circular path of radius . Driver of car applies the brakes producing a uniform deceleration of. Then,
A) The centripetal acceleration of car just after applying the brake is 4 m/s².
B) The acceleration just after applying the brake is 5 m/s².
C) The acceleration is directed towards the centre just after applying the brake.
D) The angle between acceleration and velocity just after applying the brake is 127.
The speed of a particle in a circle is along the circumferences of a circle of radius. If the speed increases at the rate of . The acceleration of the particle at a given instant